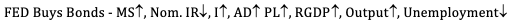Quick - Limited Reserves - Monetary Policy
Saturday, November 5, 2022
Quick - LImited Reserves. Monetary Policy
Quick - Ample Reserves - MOnetary POlicy
Quick - Ample Reserves - MOnetary POlicy
Monday, October 31, 2022
IB 2022 Economics Higher Level Paper 3
IB Economics Higher Level Paper 3
2. Asepsis Corp. operates in an imperfectly competitive industry producing hand sanitizer called Sani-Gel. The company currently produces the profit-maximizing quantity of Sani-Gel but is operating at a loss. [4]
(a) Draw a correctly labeled graph for Asepsis Corp. and show
-
(i) The profit - maximizing output, labeled as QM
-
(ii) The profit - maximizing price, Labeled as PM
-
(iii) The area of loss shaded completely
(b) Assume that Asepsis is operating in the short-run. Amend the diagram from part a) AND write an explanation in the box below to demonstrate how the firm can remain open in the short-run while still operating at a loss.
3. (a) Complete the following table for McLovin’s:
(b) Identify and explain the point at which McLovin’s begins to experience the law of diminishing returns
4. The table below shows the total costs of production for STC Inc.
|
Output (Lbs) |
Total Costs ($) |
|
0 |
15,000 |
|
50 |
25,000 |
|
100 |
33,000 |
|
150 |
39,000 |
(a) State the value of STCInc.’s fixed costs.
(a) If the output is zero and there is a (TC) total cost - then that has to be Fixed Costs
When output is zero it implies that the Variable Costs is zero but Fixed Costs are 15k.
(b) Calculate the value of STC Inc.’s average variable cost if it produces 100 Lbs of output.
With an output of 100 lbs the TC is 33K - 15k (FC) = VC = 18k
(c) With reference to the data in the table, explain why STC Inc. achieves increasing returns to scale as it increases output from 50 Lbs to 150 Lbs.
Saturday, September 17, 2022
ALL "Released"Price Floor & Price Ceiling Multiple Choice Questions
ALL "Released"Price Floor & Price Ceiling
Multiple Choice Questions
ALL Released Multiple Choice Questions Indirect Tax
Released Multiple Choice Questions
Indirect Tax
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HlKLu8K94QQ
Saturday, February 19, 2022
FED - T Accounts Multiple Choice Review (Released AP exam questions)
Federal Reserve - Central Bank - Monetary Policy
Past AP Exam (Released) Questions
Multiple Choice Review